Trading is never completely risk-free: markets move quickly, leverage can magnify losses, and beginners often underestimate volatility. Many traders lose money because they ignore key risks or trade without a clear plan.
In this guide, you’ll learn the major trading risks, why losses happen, and practical steps to protect your capital and trade more confidently.
Is Trading Safe?
The short answer: not entirely. All financial markets carry risk, and even experienced traders can face losses. Trading safely means understanding these risks and preparing for them before placing any trades. By knowing what can go wrong, you can reduce surprises and make informed decisions.
Tip: Treat trading like a skill that requires study and practice — not gambling.
Major Risks in Trading
Trading involves several core risks that every beginner should understand:
Market Volatility
Prices can swing dramatically in short periods. Unexpected news, economic events, or market sentiment can move markets against your position.
Example: If EUR/USD moves 100 pips in a single day and you hold a leveraged position, your account balance can swing 10–20%.
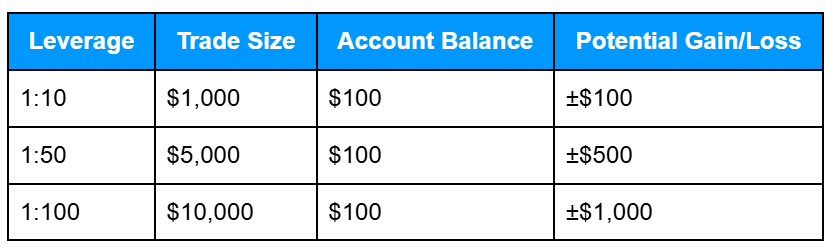
Leverage Risk
Using leverage amplifies both profits and losses. Even a small price movement can have a big impact on your account.
Slippage
Sometimes trades execute at a different price than you requested, especially during fast-moving markets or low liquidity.
Example: You place a buy order for BTC/USD at $30,000, but it executes at $30,050. That $50 difference reduces your expected profit.
Liquidity Risk
Low liquidity means fewer active buyers and sellers, which can cause wider spreads or difficulty filling your order at the price you want.
Example: You try to close a CFD position on a minor stock index during the Asian session. The spread widens from 1 point to 6 points because there are fewer participants. Instead of exiting at 4,500.0, your order fills at 4,494.0, a 6-point difference that increases your loss.
Tip: Trade highly liquid instruments or during peak market hours to reduce execution risk.
Emotional & Psychological Risk
Human behaviour contributes heavily to trading losses. Fear, greed, impatience, or overconfidence often override logic. Here are some examples:
Fear: The market moves slightly against your position, and you close the trade early to “avoid a bigger loss.” Minutes later, the price rebounds and hits your original take-profit level.
Greed/overconfidence: You have two winning trades in a row and decide to double your next position size. A small pullback wipes out your previous profits and more.
Chasing losses: After a losing trade, you immediately open a new, larger position to recover quickly. The rushed decision leads to another loss, compounding the damage.
Tip: Predetermine your entry, exit, and stop-loss levels before you enter the trade so emotions can’t override your plan.
Why Traders Lose Money
Many beginners fail not because trading is impossible, but because of psychological and strategic errors:
- Emotional Trading: Fear and greed drive impulsive decisions. For example, panicking during a small market dip can lead to unnecessary losses.
- Lack of Strategy: Trading without a plan often results in inconsistent outcomes. A written plan with defined entries, exits, and risk per trade keeps you disciplined.
- Ignoring Risk Management: Over-leveraging, neglecting stop-losses, or putting too much capital into one trade can turn small losses into major setbacks.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
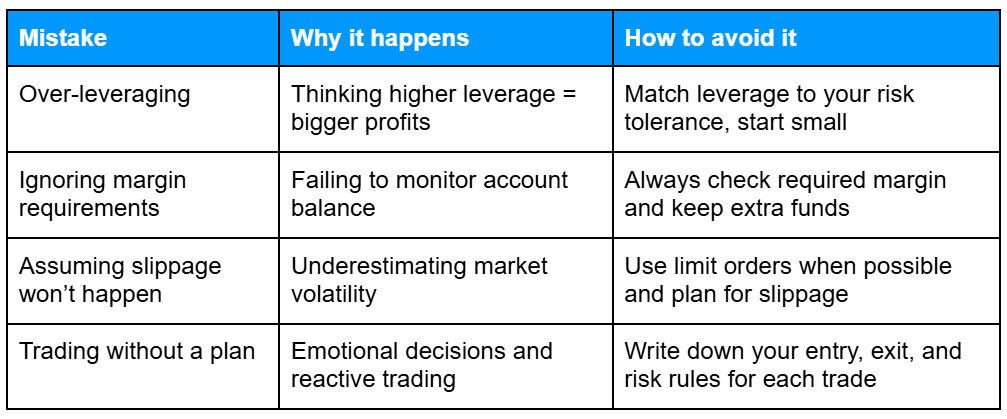
Tip: Start with small positions to understand mechanics before risking larger amounts.
Practical Risk Management Tips
- Set stop-loss orders: Limit losses automatically and reduce emotional decision-making.
- Use proper position sizing: Never risk more than a small percentage of your account on a single trade.
- Diversify your trades: Avoid putting all your capital into one asset or trade.
- Keep a trading journal: Track your trades, mistakes, and lessons learned to improve over time.
- Educate yourself continuously: Study the markets, trading strategies, and mechanics before increasing exposure.
Tip: For each trade, ask: “What is the maximum I’m willing to lose?”, then plan your stop-loss and position size accordingly.
Using Your Platform Safely (MT4/MT5 or Broker Tools)
Most CFD brokers provide platforms like MT4 or MT5, which help you:
- Monitor margin levels in real-time
- Set leverage for each trade
- Track executed vs requested prices
- Place stop-loss and take-profit orders
Tip: Use a demo account to practice risk management techniques and understand how platform tools work before trading live.
Related Articles and Further Reading
- What is a CFD? Understanding Pips, Lots & Spreads
- Leverage, Margin & Slippage: How They Affect Your CFD Trades
- Risk-to-Reward Ratios & Practical Strategies: Applying Risk Management in Real Trades
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is trading safe?
A: Trading is never completely risk-free. Understanding the risks and using proper risk management helps you trade more safely.
Q: What are the risks of trading?
A: Main risks include market volatility, leverage, slippage, and emotional decision-making. Knowing these helps you plan your trades better.
Q: Why do most traders lose money?
A: Many lose due to poor risk management, over-leveraging, or trading without a clear strategy. Practicing discipline and preparation can reduce losses.
Next Steps
Want to learn more?
Find out how to apply risk management in real trades in our article on risk-to-reward ratios.