Forex trading is the global exchange of currencies, where every trade involves buying one currency while selling another. To trade successfully, you need to understand how forex works, how currency pairs are structured, and what factors influence their prices.
In this guide, you’ll learn about forex trading basics, including currency pair mechanics, how profits and losses are calculated, and common mistakes beginners should avoid. By the end, you’ll have the foundation to explore more advanced topics like leverage, margin, and trading strategies.
What Is Forex Trading?
Forex, short for foreign exchange, is the world’s largest financial market. It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across major financial centers such as London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney.
Unlike stock markets, forex doesn’t have a central exchange. It’s an over-the-counter (OTC) market, meaning trades are conducted directly between participants.
Understanding who trades forex helps you see why prices move the way they do.
Who Trades Forex?
- Banks and financial institutions manage the flow of global currencies for international operations.
- Hedge funds and professional traders aim to profit from short-term price movements.
- Companies hedge currency risk in global business transactions.
- Retail traders like you can access the market online through brokers and trading platforms like MT4 or MT5.
Why Do People Trade Forex?
- Speculation: Traders aim to profit from changes in currency values.
- Hedging: Businesses and investors protect against currency fluctuations.
- International trade: Companies exchange currencies to pay for imports, exports, or overseas operations.
Example:
If EUR/USD moves from 1.0800 to 1.0850, the euro has strengthened relative to the US dollar. A buy trade on EUR/USD would profit from this movement.
Think of forex like exchanging money before a holiday. If you convert USD to EUR and later convert back at a better rate, you earn a profit. Forex trading works the same way but online, with the goal of making money from price changes.
How Forex Trading Works
Forex trading involves buying and selling currency pairs at fluctuating exchange rates.
Trading Exchange Rates
The price shows how much of the quote currency you need to buy one unit of the base currency.
Example:
EUR/USD at 1.0850 → 1 EUR = 1.0850 USD.
Market Hours and Liquidity
Forex is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, with four main trading sessions: Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York. Session overlaps, such as London/New York, often see higher liquidity and tighter spreads, making it easier to enter or exit trades at your desired price.
Tip: Beginners often trade during the London/New York overlap for better execution and tighter spreads.
Brokers & Trading Platforms
Platforms like MT4/MT5 let you:
- Place trades (market or pending orders)
- View charts and technical indicators
- Set stop-loss and take-profit levels
- Monitor margin and account balance
Example:
You decide to buy EUR/USD: set a stop-loss 20 pips below your entry and a take-profit 40 pips above. As the price moves, you can watch your trade progress in real time and adjust if needed.
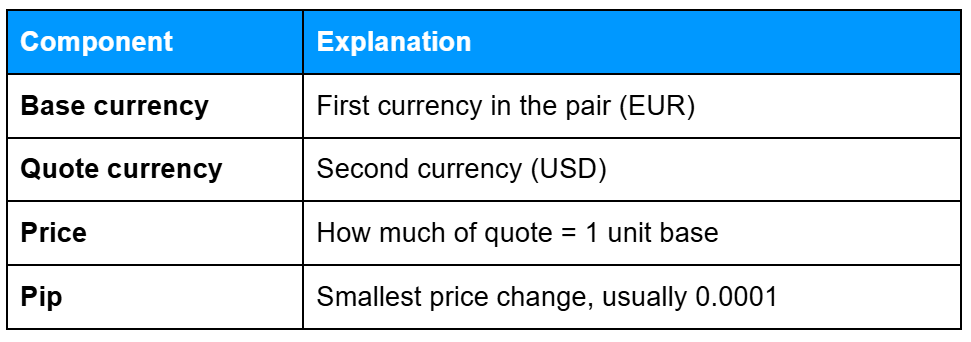
What Is a Currency Pair?
A currency pair shows the relationship between two currencies: the base currency (the one you buy or sell) and the quote currency (used to measure its value). Every forex trade involves exchanging one currency for another.
Currency Pair Components
Why Currency Pairs Exist
Currencies are always traded in pairs because you are always exchanging one currency for another. Think of it like converting money before a trip: you can’t buy euros without paying in dollars (or another currency).
Long vs Short: How You Profit
In forex, price movement in either direction can create trading opportunities. What matters is whether you expect the base currency to strengthen or weaken.
- Going long (buying the base): You expect the base currency to strengthen relative to the quote currency.
- Going short (selling the base): You expect the base currency to weaken relative to the quote currency.
Examples:
- Long trade: EUR/USD at 1.0800, you buy 1,000 EUR. Price rises to 1.0820 → 20-pip profit.
- Short trade: EUR/USD at 1.0800, you sell 1,000 EUR. Price drops to 1.0780 → 20-pip profit.
Tip: Always calculate potential profit and loss in the quote currency before entering a trade.
Major, Minor & Exotic Currency Pairs
Different categories of currency pairs tend to behave differently in terms of cost, liquidity, and volatility, so it’s useful to understand how each one trades.
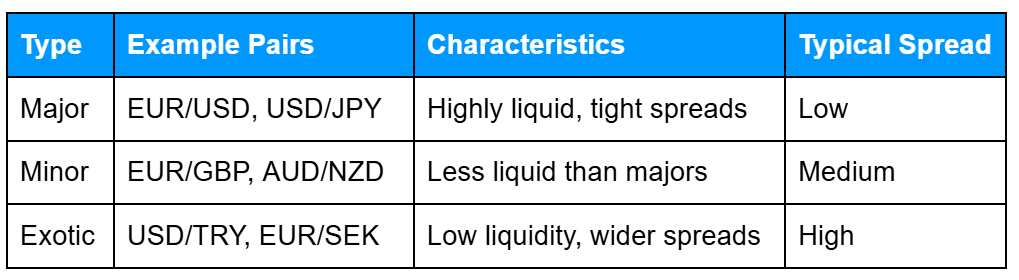
Quick takeaways:
- Majors: Most traded, tighter spreads, easy to enter/exit trades.
- Minors: Moderate liquidity and cost, slightly riskier than majors.
- Exotics: Can be volatile and expensive to trade; usually best avoided when starting out.
What Moves Forex Prices?
Forex prices mainly move because of changes in supply and demand for currencies. Several core factors drive this:
Interest Rates
Higher interest rates usually attract foreign investment because investors look for higher returns. This can strengthen a currency, while lower rates tend to have the opposite effect.
Example:
If the US increases interest rates → investors may buy more USD → USD strengthens.
Central Bank Policies
Central banks control interest rates, money supply and may intervene in markets. Their announcements can cause large moves, especially if unexpected.
Watch closely:
- US Federal Reserve
- European Central Bank
- Bank of England
- Bank of Japan
Economic Data
GDP, unemployment, inflation (CPI), PMI can affect market sentiment. Stronger data usually supports the currency, weaker pushes it lower.
Stronger-than-expected results usually support the currency, while weak results can push it lower.
Market Sentiment & Geopolitics
Risk appetite, elections, conflicts, trade relations, or crises can drive volatility. Traders may seek “safe-haven” currencies like USD, JPY, CHF during uncertainty.
Tip: Plan trades around economic calendars and be aware of possible slippage or gaps.
Forex Example Calculation
Understanding how pip movement converts into actual profit/loss helps you assess trade impact before you enter a position. Even small changes in price (and spread cost) can make a noticeable difference once you scale up order size.
Pip Movement Example:
1 pip = 0.0001 for most pairs.
- Buy 1,000 EUR/USD at 1.0800
- Sell at 1.0820 → 20 pips
- Pip value ≈ $0.10 per pip → Profit = $2
Spread Impact: If spread = 2 pips → real net = $1.80
Tip: Testing small trade sizes is a simple way to understand pip values, spread costs, and emotional swings without taking unnecessary risk.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced traders refine their approach over time, and some challenges tend to appear early in the learning curve. These patterns are normal, and understanding them helps you make more confident decisions.
Mistake: Trading too large too soon
Solution: Start with micro-lots until consistent.
Mistake: Trading news volatility
Solution: Wait 10–15 minutes after major releases.
Mistake: Ignoring costs (spread/swap)
Solution: Always check before opening a position.
Mistake: High leverage
Solution: Set a max leverage cap; increase gradually as experience grows.
Tip: Think of mistakes as part of the learning curve. Even professional traders started small and learned from each trade.
Key Forex Risks
Trading forex involves several risks that can affect both your profits and losses. Understanding these key risks helps you manage your trades more effectively and protect your account from unexpected moves.
Volatility
Forex prices can move quickly, especially during news releases or overlapping sessions. These sudden moves mean both profits and losses can build faster than expected. That’s why beginners typically trade smaller position sizes and always pre-define risk per trade.
Liquidity
Major pairs are usually highly liquid, but minor and exotic pairs can have wider spreads and slower execution. This affects your actual entry and exit price. When learning, most traders focus on majors because they’re cheaper to trade and behave more predictably.
Leverage
Forex uses margin, which lets you control a large position with a relatively small deposit. This can magnify profits, but it can also magnify losses. High leverage is one of the main reasons beginners blow accounts early, so it’s smart to use lower leverage until you’re confident managing risk.
Overnight Exposure & Gaps
Markets can “gap” after major announcements or between sessions, meaning price can open significantly higher or lower than where it closed. In rare cases, stop-loss orders may fill at a worse price than expected. If you keep trades overnight, be aware of potential swap costs and price gaps.
Tip: Always set stop-loss levels and use manageable position sizes.
Using Your Platform Safely
Most brokers provide platforms like MT4 or MT5, which help you trade efficiently and manage risk. With these tools, you can:
- Monitor margin levels and available funds in real time
- Set leverage for each trade according to your risk tolerance
- Track executed prices versus requested prices
- Place stop-loss and take-profit orders to protect capital
Tip: Practice on a demo account to understand platform tools, test strategies, and apply risk management before trading live.
Frequently Asked Questions About Forex Trading
Q: How does forex trading work?
A: You buy one currency and sell another at a current exchange rate, aiming to profit from price changes.
Q: What are currency pairs?
A: Two currencies traded together; one is the base and one is the quote.
Q: What is a pip?
A: The smallest price increment in a currency pair, usually 0.0001 for most pairs.
Q: Why do exchange rates move?
A: Interest rates, central bank policies, economic news, and market sentiment all affect rates.
Related Articles and Further Reading
- Forex Mechanics: Leverage, Position Sizing & How Execution Works
- Forex Trading Costs: Swaps, Overnight Fees & Slippage
- Forex Risk & Profitability: Factors Affecting Prices, Trading Risks & Safe Strategies
Next Steps
Want to learn more?
Find out how leverage, position sizing and trade execution work in our article on forex mechanics.