Cryptocurrency trading can seem complex at first, with different assets, trading methods, and technology to understand. Knowing how cryptocurrencies work, how spot crypto trading differs from crypto CFDs, and the basics of blockchain helps you make informed decisions and stay aware of risk.
This guide explains these concepts with clear examples, practical tips, and straightforward risk considerations.
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital form of money that operates without a central authority. It uses encryption and blockchain technology to secure transactions and maintain a decentralized ledger. Popular examples include Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Litecoin (LTC).
At a basic level, cryptocurrencies share a few defining characteristics:
- Digital: Exists only electronically and is stored in digital wallets.
- Decentralized: Operates on distributed networks instead of being issued by governments or central banks.
- Secure: Transactions are encrypted and recorded on a public blockchain, making them tamper-resistant.
Think of cryptocurrency like digital cash: you can send it directly to someone else, and the blockchain acts as a public, tamper-proof ledger that verifies every transaction.
People use cryptocurrencies to store value, make payments, or trade, all without relying on a central authority.
What is Crypto CFD Trading?
A Crypto CFD (Contract for Difference) is a financial derivative that allows you to speculate on the price of a cryptocurrency without owning the underlying asset. Instead of buying the coin itself, you enter a contract with a broker to gain exposure to price movements.
Crypto CFDs involve a few key features:
- Leverage: CFDs let you trade larger positions than your account balance would normally allow. While this can amplify gains, it also increases potential losses.
- Long and short positions: You can take positions that profit from both rising and falling prices.
- Margin requirements: You only need to deposit a fraction of the position’s total value to open a trade, but you must maintain sufficient margin to keep the position open.
Risk awareness: Because CFDs use leverage, losses can exceed your initial deposit if risk is not managed carefully. Always calculate your exposure, use position sizing, and set stop-losses to help manage risk effectively.
What Are The Key Differences Between Spot And CFD Crypto?
Spot trading and CFDs differ in several key ways, including ownership, leverage, and how trades are executed.
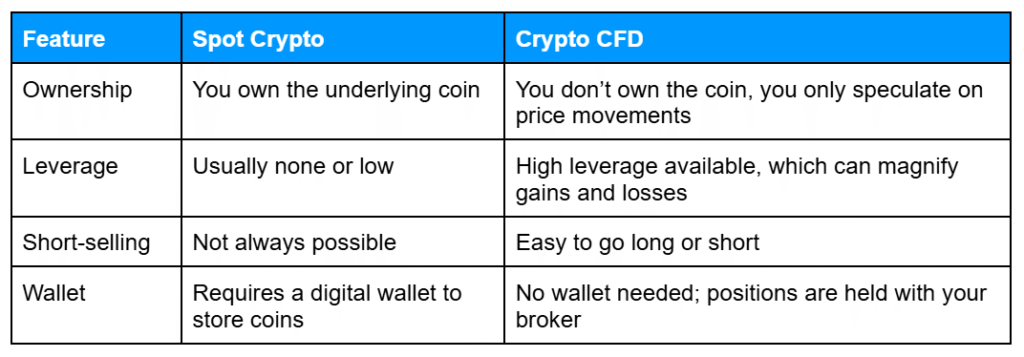
Spot trading is often chosen by those who want direct ownership of cryptocurrency, while CFDs are typically used by traders who want flexibility and the ability to trade both rising and falling markets. Both approaches carry risk: leverage in CFDs can amplify losses, and spot trading is still exposed to market volatility.
How Does Crypto Trading Work?
Crypto trading works differently depending on whether you buy the cryptocurrency directly (spot trading) or trade its price using derivatives like CFDs.
Spot Trading
When you trade crypto on the spot market, you buy the actual cryptocurrency on an exchange and store it in a digital wallet. Your profit or loss comes from changes in the coin’s price.
Example:
Buy 1 BTC at $30,000, sell at $31,500 → exposure to a $1,500 price change.
Crypto CFDs
With crypto CFDs, you enter a contract with a broker to speculate on price movements without owning the underlying asset. Leverage allows you to open larger positions than your account balance, which can increase both potential gains and potential losses.
Example:
Open a $10,000 CFD position with 10:1 leverage. A 5% price movement changes your position by $5,000 (before fees and spreads).
Market Considerations
Crypto markets operate 24/7 and can be highly volatile. Costs such as spreads and slippage can reduce net results, and leveraged positions can magnify both gains and losses. Using risk controls like stop-losses, position sizing, and careful exposure management helps you navigate these challenges.
Factors That Influence Prices
Cryptocurrency prices are affected by supply and demand, adoption by individuals and businesses, news events, regulatory developments, and overall liquidity. Understanding these drivers can help you anticipate why prices move, even if you don’t trade actively, and reinforces the importance of risk management in volatile markets.
Volatility in Action
Imagine you open a $5,000 CFD position on Bitcoin with 5:1 leverage. A 4% price movement against your position would result in a $1,000 loss, which is 20% of your initial deposit.
The same price movement in a spot position would only change your holding by 4%, showing how leverage can magnify both gains and losses. Scenarios like this highlight the importance of position sizing, stop-losses, and careful exposure management.
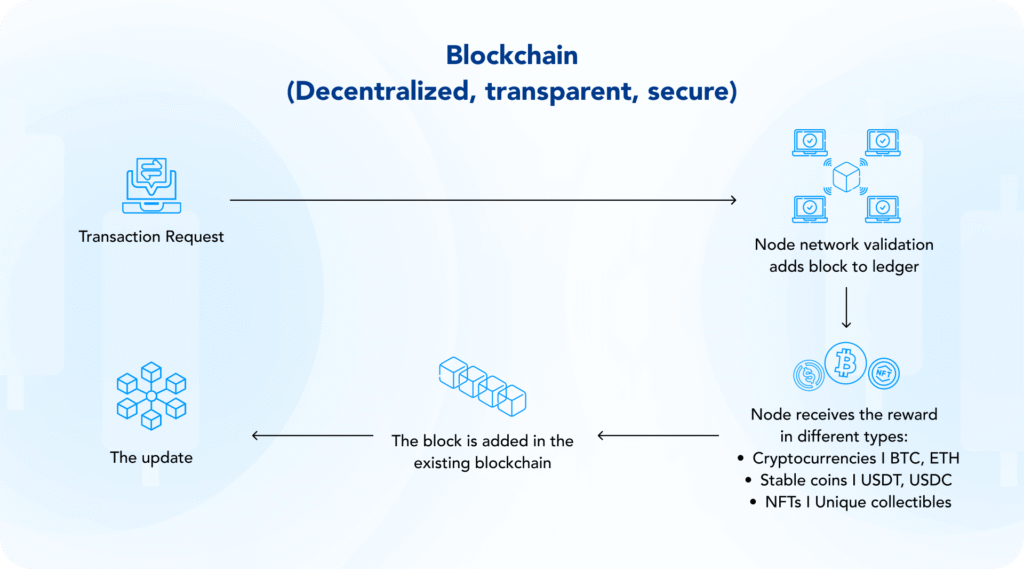
Blockchain and Digital Assets Explained
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records all cryptocurrency transactions. It provides a secure and transparent way to track transactions without relying on a central authority.
At a basic level, blockchain offers three key benefits:
- Decentralization: No single authority controls the system; it operates across a distributed network.
- Transparency: Every transaction is publicly recorded and can be verified by participants.
- Security: Cryptography ensures that data cannot be tampered with once recorded.
Digital assets beyond cryptocurrencies
The blockchain ecosystem also supports a range of other digital assets:
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): Unique digital collectibles or assets.
- Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies, such as USDT or USDC, designed to reduce volatility.
- Tokens: Digital representations of value or utility within a blockchain network.
Here’s a simple overview of blockchain mechanics and the main types of digital assets built on the network.
Practical Tips & Common Misconceptions
Before trading with real funds, consider these steps to help manage risk and stay disciplined:
- Start with a demo account: Practice trading in a simulated environment to understand mechanics without risking real money.
- Know the differences between spot and CFDs: Understand how ownership, leverage, and trade execution affect your exposure.
- Apply risk management: Use stop-losses, position sizing, and leverage limits to control potential losses.
- Keep a trading journal: Track your trades, strategies, and mistakes to learn from experience.
- Monitor costs carefully: Spreads, fees, and slippage can affect net results.
- Avoid emotional trading: Stick to your plan and strategy rather than reacting impulsively to market movements.
It’s also important to be aware of some common misconceptions in crypto trading. CFDs are not risk-free as leverage can amplify losses beyond your initial investment.
Similarly, spot trading is not inherently safer, since holding the underlying cryptocurrency still exposes you to market volatility and potential losses. Keeping these points in mind can help you approach trading more cautiously and make informed decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is crypto CFD trading?
A: A crypto CFD (Contract for Difference) is a financial derivative that allows you to speculate on cryptocurrency price movements without owning the underlying coin.
Q: How do crypto CFDs differ from spot crypto?
A: CFDs offer leverage and allow you to take both long and short positions. Spot trading requires ownership of the cryptocurrency and usually does not involve leverage.
Q: What is cryptocurrency?
A: Cryptocurrency is digital money secured by blockchain technology. It is decentralized, transparent, and can be transferred directly between users without a central authority.
Q: How does crypto trading work?
A: In spot trading, you buy and hold the actual cryptocurrency, profiting or losing based on price changes. With CFDs, you open a contract with a broker to speculate on price movements, often using leverage that can amplify gains and losses.
Q: What are blockchain and digital assets?
A: Blockchain is a secure, decentralized ledger that records all cryptocurrency transactions. Digital assets include cryptocurrencies, tokens, stablecoins, and NFTs, each with different characteristics and uses on the blockchain.
Related Articles
- Crypto CFD Mechanics: How Trading and Leverage Work
- Crypto Market Factors: Understanding Volatility and Price Drivers
- Crypto Risk & Safety: Understanding Trading Risks, Profitability, and Safety Tips
Next Steps
Want to learn more?
Find out how trading crypto CFDs and leverage work in our crypto CFD mechanics primer.