Trading crypto CFDs allows you to speculate on cryptocurrency price movements without owning the underlying coins. To trade effectively, it’s important to understand how CFDs work, how leverage can amplify both gains and losses, and how trades are managed in practice.
This guide breaks down core crypto CFD mechanics, including leverage, margin, and long and short positions, and walks through how a typical trade is set up. Along the way, it highlights practical considerations and risk-awareness tips to help you approach leveraged trading more carefully.
What is Crypto CFD Trading?
A Contract for Difference (CFD) is a derivative that lets you trade cryptocurrency price movements without owning the underlying asset. Instead of buying or selling the coin itself, you enter a contract that reflects how its price changes over time.
When trading crypto CFDs, a few core mechanics come into play:
No ownership of the asset
You do not hold the cryptocurrency. Your position is based solely on price movement, not possession of the coin.
Use of leverage
CFDs allow you to control a larger position than your initial deposit. This can increase potential gains, but it also magnifies losses if the market moves against you.
Ability to go long or short
You can take positions that benefit from both rising and falling prices, depending on your market view.
Margin requirements
Opening and maintaining a CFD position requires sufficient margin in your account. If your margin falls too low, positions may be reduced or closed.
Because leverage amplifies exposure, it’s important to calculate position size carefully and understand how much of your capital is at risk before entering a trade.
How Does Leverage Work in Crypto CFDs?
Leverage allows you to open a larger trading position using a smaller amount of capital, increasing your exposure to price movements.
Example:
- Account balance: $1,000
- Leverage used: 10:1
- Total position size: $10,000
If the market moves 5%, the position changes by $500, resulting in either a gain or a loss equal to 50% of your account balance, before fees and spreads.
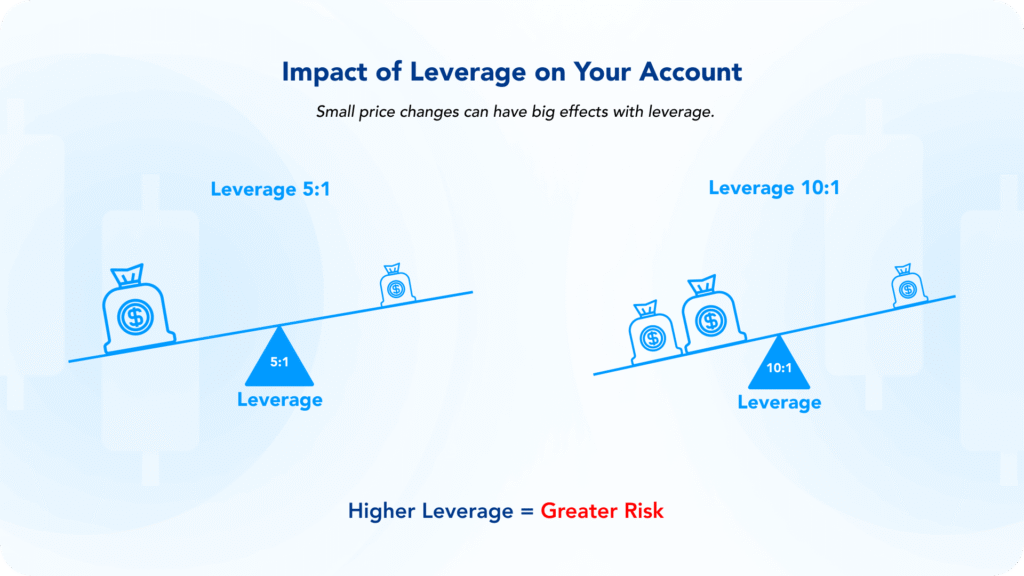
In practice, this means leverage can accelerate results in both directions.
When using leverage, it’s worth keeping a few points in mind:
- Higher leverage increases potential profits, but it also increases potential losses.
- Leverage levels should reflect your risk tolerance, account size, and trading experience.
- Crypto markets can be highly volatile, so price swings may affect leveraged positions quickly.
Key Differences Between Spot and CFD Crypto
Spot trading and CFDs differ in how you hold and trade cryptocurrency. Understanding these differences helps you choose the approach that matches your goals and risk tolerance.
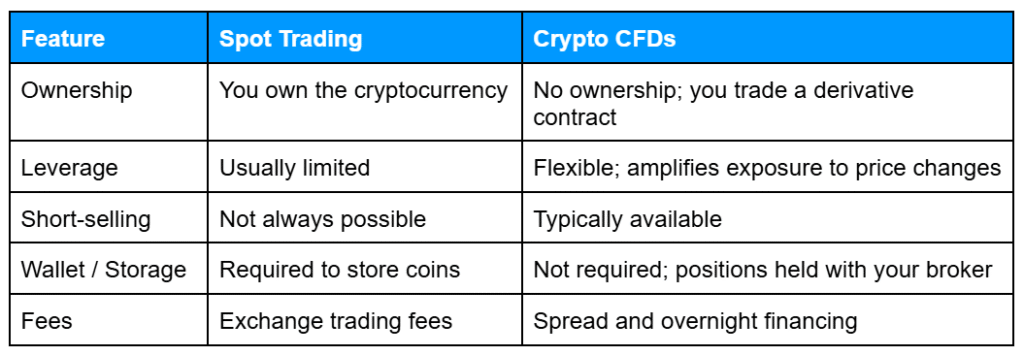
CFDs are generally suited for traders who want flexibility, leverage, and the ability to go short without managing wallets. Spot trading is better for those focused on long-term holding and direct ownership of cryptocurrency.
How Crypto CFD Trading Works
Crypto CFD trading follows a structured process, from opening a position through a broker to managing it as prices move. While the mechanics are similar to other CFD markets, crypto’s volatility and 24/7 trading add additional considerations.
Opening a Crypto CFD Trade
When you trade crypto CFDs, you place orders through a broker rather than buying cryptocurrency directly from an exchange. You choose whether to go long or short, set your position size and leverage, and place an order using market, limit, or stop orders.
Once the trade is opened, margin is allocated from your account to support the position.
Managing an Open Position
While a position is open, its profit or loss changes in real time as the crypto price moves. Stop-loss and take-profit orders can be used to manage exits and control risk, though fast market conditions may affect execution.
Because crypto CFDs trade 24/7, price movements can occur at any time, including outside traditional market hours.
Example:
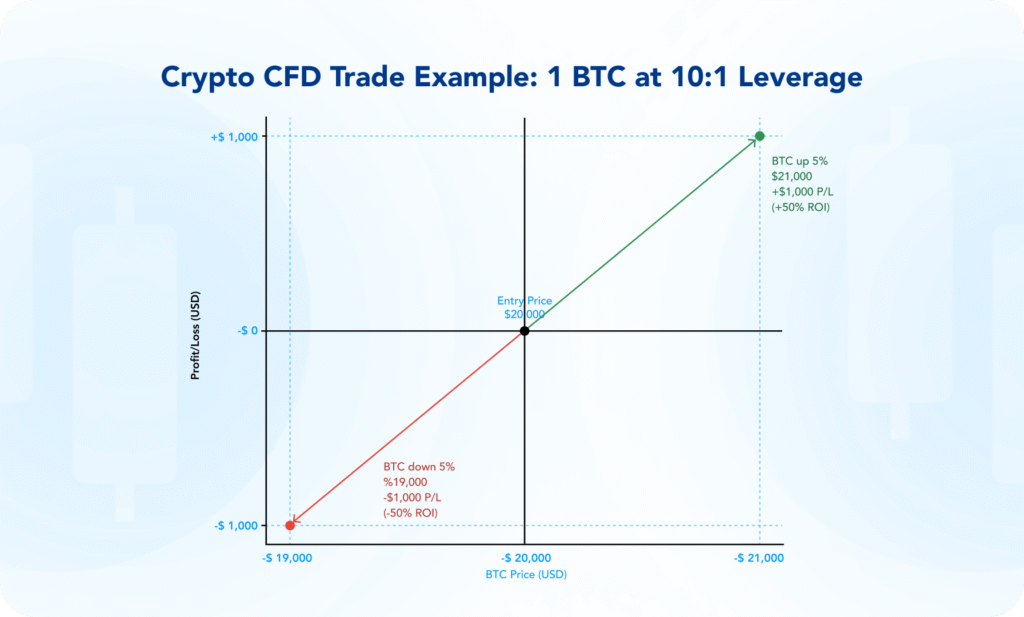
Imagine opening a long CFD position equivalent to 1 BTC at $20,000, using 1:10 leverage.
If Bitcoin’s price rises 5% to $21,000, the position increases by $1,000, which represents a 50% change relative to the margin used, before fees and spreads.
This example shows leverage magnifies gains and losses relative to your margin.
Because crypto markets can move rapidly, managing risk is an ongoing part of CFD trading. Monitoring margin levels, adjusting position size, and using protective orders can help manage exposure, although they do not remove risk entirely.
Step-by-Step Guidance for Crypto CFD Trades
Once you understand the mechanics of crypto CFDs, the next step is seeing how a trade unfolds in practice. From setting up your account to monitoring an open position, each stage has specific considerations that help you manage exposure and make informed decisions.
1. Account setup and funding
Why: You need a properly funded account to support trades and meet margin requirements.
Open an account with a regulated broker that offers crypto CFDs. Fund the account and review margin requirements, which determine how much capital is needed to open and maintain positions.
2. Market selection and exposure planning
Why: Choosing the right market and position size defines your potential gains and losses.
Select a cryptocurrency and decide on position size and leverage. Consider how price movements could impact your account and risk exposure.
3. Placing the trade
Why: Proper entry and risk controls can protect your capital from large losses.
Place a long or short order via the trading platform. Add stop-loss and take-profit orders to manage exits and control downside risk.
4. Monitoring and managing the position
Why: Crypto markets move quickly, and active monitoring helps you adapt to changing conditions.
Track your position as prices move. Adjust risk controls, reduce exposure, or close the trade to realize profits or limit losses.
For those new to leveraged trading, using a demo account can help build familiarity with CFD mechanics and leverage before trading with real funds.
Common Mistakes in Crypto CFD Trading
Trading crypto CFDs can be complex, and certain errors are more likely to result in losses. Common pitfalls include:
- Excessive leverage: Amplifies losses if used without understanding exposure.
- Ignoring trading costs: Spreads, swap/financing fees, and other charges can eat into profits.
- Skipping stop-loss orders: Can result in larger-than-intended losses.
- Emotional trading: Chasing losses or reacting impulsively undermines discipline.
- Mixing spot and CFD mechanics: Spot involves owning coins; CFDs are derivatives. Confusing them can misjudge risk.
Tip: A clear trading plan and disciplined risk management are more important than any particular strategy.
Practical Examples of Risk Management
Understanding common mistakes is one thing, but seeing how they play out in practice helps make risk more tangible. Leverage can dramatically magnify both gains and losses. For example:
- Suppose you have a $2,000 account and open a $10,000 BTC CFD long position using 5:1 leverage.
- If Bitcoin’s price moves 4% against you, the position loses $400, which is 20% of your account balance.
To manage these risks, traders often:
- Use smaller position sizes to limit potential losses
- Set stop-loss orders aligned with risk tolerance
- Take market volatility and major events into account before entering trades
These steps help traders approach leveraged crypto CFD positions more cautiously while keeping potential losses within manageable levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a crypto CFD?
A: A crypto CFD (Contract for Difference) is a financial derivative that lets you speculate on cryptocurrency price movements without actually owning the coin.
Q: How does leverage affect my crypto CFD trades?
A: Leverage amplifies the size of your trades relative to your deposit. This can increase both potential profits and potential losses.
Q: Can I go short with crypto CFDs?
A: Yes. CFDs allow you to profit from falling prices, unlike spot trading, which may limit short-selling opportunities.
Q: Do I need a crypto wallet for CFDs?
A: No. Because you don’t hold the underlying asset, you don’t need a wallet to trade CFDs.
Q: What are the main risks in crypto CFD trading?
A: Crypto CFDs carry high volatility, leverage risk, and the potential for gaps in market prices. Using risk management tools like stop-losses and careful position sizing is essential to protect your capital.
Related Articles
- Crypto Trading Basics: Spot vs CFD and Blockchain Explained
- Crypto Market Factors: Understanding Volatility and Price Drivers
- Crypto Risk & Safety: Understanding Trading Risks, Profitability, and Safety Tips
Next Steps
Want to learn more?
Find out how volatility and price drivers work in our article on crypto market factors.