What Affects the Price of Gold?
Gold prices are influenced by a mix of macroeconomic factors, market sentiment, and supply-demand dynamics. Understanding these drivers can help traders interpret market movements more effectively.
USD Strength
Gold often moves inversely to the US dollar. When the dollar strengthens, gold becomes more expensive for investors using other currencies, which can reduce demand.
Inflation and Interest Rates
Rising inflation or lower interest rates can increase gold’s appeal as a store of value. Conversely, higher interest rates may make interest-bearing assets more attractive, reducing gold demand.
Central Bank Policies
Gold prices can be affected by central bank actions such as buying or selling gold reserves, as well as broader monetary policy decisions that influence market perception.
Global Uncertainty
Political or economic instability, geopolitical tensions, and market crises can increase demand for gold as a safe-haven asset, often driving price spikes.
Supply and Demand
Factors such as mining output, recycling activity, and jewelry demand shape gold’s long-term supply and demand balance, influencing prices over time.
To provide a quick overview, the table below summarizes the main factors that influence gold prices, how they affect the market, and key considerations for traders.
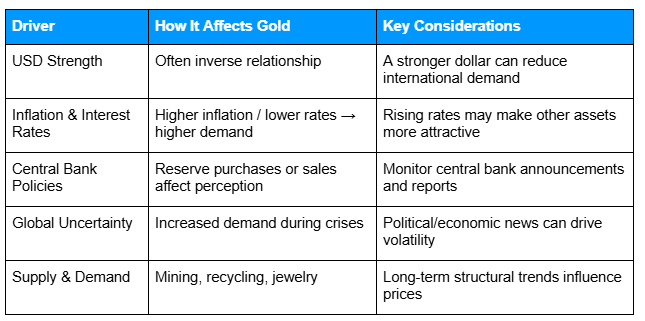
Alt text: Table listing major factors that affect precious metals prices specifically for gold, including US dollar strength, inflation and interest rates, central bank actions, global uncertainty, and supply and demand
What Affects the Price of Silver?
Silver shares some price drivers with gold but also has unique industrial and investment influences. Understanding these factors helps traders interpret short- and long-term price movements when trading silver CFDs.
Industrial Demand
Silver is widely used in electronics, solar panels, and other manufacturing processes. Changes in industrial demand can significantly influence silver prices.
Investment Demand
Investors also hold silver in the form of ETFs, coins, or physical bullion. Shifts in investor interest can create additional price movements, sometimes independent of industrial trends.
Economic Indicators
Silver responds to broader economic factors such as inflation, interest rates, and USD strength, similar to gold. These indicators can affect both investment and industrial demand.
Supply Constraints
Mining output, recycling activity, and geopolitical events can restrict or expand supply, impacting prices over time.
Volatility
Due to its smaller market size relative to gold, silver often experiences sharper short-term price swings. Traders using CFDs should be aware that volatility can amplify both gains and losses.
To provide a quick comparison, the table below highlights key drivers for silver, how they affect prices, and notes for traders. Gold is included for reference to illustrate differences in market influences.
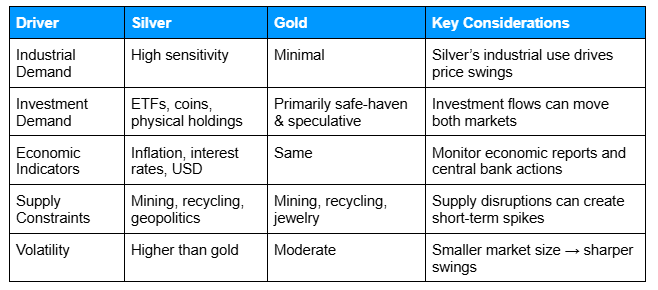
Alt text: Table comparing silver and gold price drivers, including industrial demand, investment demand, supply constraints, and volatility, with key considerations for each.
How to Start Trading Gold and Silver CFDs
Understanding what drives gold and silver prices is the first step. The next is knowing how to trade CFDs and manage risks at each stage.
1. Open a CFD Account with a Regulated Broker
Choose a broker offering metals CFDs and tools such as stop-loss orders, margin monitoring, and risk management features.
2. Choose a Metal to Trade
Decide between gold and silver based on your market view. Gold is typically influenced by macroeconomic factors and safe-haven demand, while silver is more sensitive to industrial demand and short-term volatility.
3. Determine Position Size and Leverage
Set a position size relative to your account balance. Leverage allows control of a larger position with a smaller deposit, but it amplifies both potential gains and losses. Always consider margin requirements and your risk tolerance.
4. Analyse Market Conditions
Use economic indicators, market news, and price charts to assess potential price movements. Key factors include USD strength, inflation data, industrial demand trends, and central bank policies.
5. Place a Long or Short CFD Position
Long position: If you expect prices to rise.
Short position: If you expect prices to fall.
CFDs allow you to trade both rising and falling markets.
6. Monitor the Trade and Manage Risk
Track market movements and adjust risk controls as needed. Stop-loss orders, exposure limits, and ongoing analysis help manage downside risk, especially during volatile periods.
7. Close the Trade and Review Performance
After closing, review the trade to understand how market drivers influenced price movements. Lessons learned can guide future decisions, though outcomes are never guaranteed.
Illustrative CFD Trade Examples
These examples are hypothetical and intended to demonstrate how market drivers may influence trading decisions. Results are not guaranteed.
Gold CFD – Long Position
- Scenario: USD weakens after softer-than-expected economic data.
- Action: Trader opens a long gold CFD.
- Outcome: Gold price rises, potentially increasing the CFD’s value. Losses may occur if the price falls instead.
Silver CFD – Short Position
- Scenario: Reports indicate a slowdown in industrial demand.
- Action: Trader opens a short silver CFD.
- Outcome: Silver prices decline, potentially benefiting the position. A price increase could result in losses.
Note: Leverage magnifies both gains and losses. Traders should carefully manage risk, particularly in volatile markets like silver.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Does gold always rise in value?
A: No. Gold prices fluctuate based on macroeconomic conditions such as interest rates, inflation expectations, and currency movements. While gold is often viewed as a store of value, it can experience periods of decline depending on market conditions.
Q: Do CFDs remove all trading risk?
A: No. CFDs are leveraged products that allow traders to gain exposure without owning the physical metal, but leverage can amplify both gains and losses. Risk management is essential when trading gold or silver CFDs.
Q: Does silver behave the same way as gold?
A: Not exactly. Although silver shares some price drivers with gold, it is more heavily influenced by industrial demand. Its smaller market size and lower liquidity can result in higher volatility and sharper short-term price movements.
Q: Does hedging guarantee protection from losses?
A: No. Hedging can help reduce exposure to certain risks, but it does not eliminate the possibility of losses. Market conditions can change quickly, and hedging strategies may not perform as expected in all scenarios.
Related Articles
Next Steps
Want to learn more?
Find out how trading gold and silver works in our precious metals CFDs trading and key concepts primer.